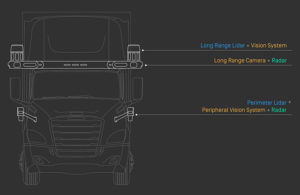
The company is proposing an innovative approach to vehicle guidance using sensors deployed within the environment, rather than just on the autonomous vehicles.
How Waymo adjusted its driver for autonomous trucking
Part of what makes Waymo’s system successful is its millions of miles of real world and simulated driving experience.
Precise motion systems drive autonomous mobile robots
Selecting the correct motor is critical to overall performance for autonomous mobile robots.
6 tips for autonomous cars to safely share roads with cyclists
Argo AI and The League of American Bicyclists released best practices for creating self-driving systems that operate safely around bicyclists.
SwRI demos drone autonomy inside nuclear power plant
SwRI’s drone was tasked with entering Austria’s Zwentendorf Nuclear Power Plant and detecting radiation sources without the aid of a human pilot or previous knowledge of the environment.
ABB upgrading AMRs with Sevensense navigation stack
ABB is installing Sevensense’s autonomous navigation technology into its mobile robots.
NASA needs your help identifying features on Mars
Improving the Soil Property and Object Classification will save NASA scientists time when planning routes for their rovers and in finding important formations.
Autobrains raises $101M for autonomous driving tech
Formerly known as Cartica AI, Autobrains is developing its modular Cartex driving platform for Level 1-4 autonomous vehicles.
How Waymo handles autonomous driving in SF
From cyclists riding against the flow of traffic to nudging over to let another car pass on a narrow street, watch a handful of typical events Waymo’s autonomous vehicles deal with in San Francisco.
BlueBotics signs distribution deal to grow Thai mobile robot market
BlueBotics claims its navigation technology is accurate to ±1 cm / ±1° and that it requires minimal changes to infrastructure.
Developing open-source systems for first responder legged robots
Project aims to take bipedal robots to a new level, equipping them to adapt on the fly to treacherous ground, dodge obstacles or decide whether a given area is safe for walking.
SLAMcore spatial intelligence software now fully supports ROS 2
New support allows full integration of vision-based 3D mapping in ROS 2 designs.
How Boston Dynamics makes Atlas run, flip & vault
A senior robotics engineer at Boston Dynamics explains how perception and adaptability enable Atlas to perform varied, high-energy behaviors like parkour.
3 tips to developing outdoor robots for unstructured environments
Scythe Robotics shares tips about sensor selection, ruggedized hardware, and software optimization for its commercial mowers.
Improved perception is pushing Atlas to new limits
By training Atlas to maneuver through complex parkour courses, Boston Dynamics developed new movements inspired by human behaviors and pushed the humanoid to new limits.
Rubble-roving robots use hands and feet to navigate treacherous terrain
University of Michigan researchers have enabled humanoid robots to use their hands in a similar way, so the robots can better travel across rough terrain, such as disaster areas or construction sites.
Training drones to avoid obstacles at high speeds
MIT developed a high-speed flight-planning algorithm that combines simulations and experiments, in a way that minimizes the number of experiments required to identify fast and safe flight paths.
Watch GE’s risk-aware autonomous robot navigate through woods
GE’s project was one of eight funded by the U.S. Army to advance autonomous, off-road navigation capabilities for military ground vehicles.
NASA: wheeled robots not enough for future space exploration
Adaptive locomotive modality, or the ability to move in different ways, is integral to extreme terrain exploration on the Moon and Mars.
From artistic vision to hardware, here’s how to make Spot dance
Engineers use a few different techniques that employed both Spot’s Choreographer software and its API to make Spot dance.
Quadruped learns to adapt to changing terrain in real time
The base policy and adaptation module are run asynchronously and at different frequencies, which allows RMA to operate robustly with only a small onboard computer.
Similarity of legs, wheels, tracks suggests target for energy-efficient robots
U.S. Army findings suggest human-made legged platforms should be as efficient as wheeled and tracked platforms.